Pest control in the food industry is crucial for maintaining hygiene, ensuring product safety, and complying with regulatory standards. Pests can contaminate food, damage products, and pose serious health risks, making effective pest management an integral part of food industry operations. Here’s a guide to essential pest control strategies for the food industry.
1. Preventive Measures
Sanitation: Cleanliness is the first line of defense against pests. Regularly clean and sanitize all areas, including food preparation surfaces, storage areas, and equipment. Ensure that spills and crumbs are promptly cleaned up and that waste is disposed of properly to avoid attracting pests.
Proper Storage: Store food products in airtight containers and keep them off the floor. Use shelving and storage practices that prevent pests from accessing food supplies. Regularly inspect stored items for signs of infestation and rotate stock to use older products first.
Facility Maintenance: Seal entry points such as shashel.eu, gaps, and holes in walls, floors, and ceilings. Ensure that doors and windows close tightly and that ventilation systems are well-maintained. Regularly inspect and repair any structural damage to prevent pests from gaining access.
2. Monitoring and Inspection
Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of your facility to identify signs of pest activity. Look for evidence such as droppings, gnaw marks, or nests. Monitoring traps and bait stations can also help detect and manage pest populations before they become a significant problem.
Pest Control Records: Maintain detailed records of pest control activities, including inspection findings, treatments applied, and any pest sightings. This documentation is essential for tracking pest issues, evaluating control measures, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
3. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM Approach: Implement an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach that combines multiple control strategies for effective pest management. IPM includes preventive measures, monitoring, and targeted treatments to manage pests while minimizing the use of chemicals.
Biological Controls: Use biological control methods, such as introducing natural predators or parasites, to manage pest populations. For example, certain insects or microorganisms can be used to target and control pests without relying solely on chemical treatments.
4. Professional Pest Control Services
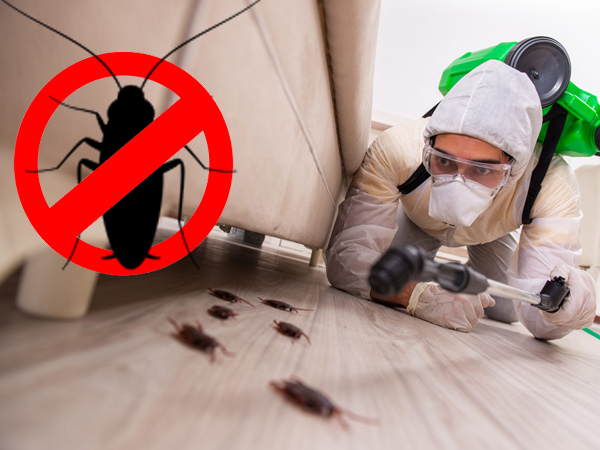
Expert Assistance: Engage professional pest control services to handle severe infestations or complex pest issues. Pest control experts can provide advanced treatments, conduct thorough inspections, and develop customized pest management plans to address specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Compliance and Certification: Ensure that pest control practices comply with industry regulations and standards, such as those set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or local health authorities. Professional pest control services are often well-versed in these requirements and can help ensure your facility meets compliance.
Conclusion
Effective pest control in the food industry involves a comprehensive approach that includes preventive measures, regular inspections, and integrated pest management strategies. By maintaining high standards of cleanliness, facility maintenance, and seeking professional help when needed, you can protect your food products, ensure safety, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.